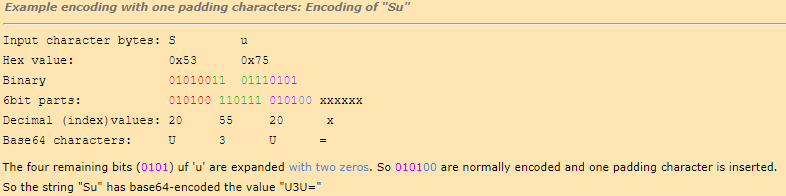Introduction
Base64 encoding is a format designed to prevent communication “mishaps” during the transfer of binary information. It achieves this through the conversion of binary data and a “lookup table” — data is eventually made in a stream of ASCII characters, which can then be transmitted and decoded. On base 64 encoded data, the resultant string is always larger than the original (i.e. this is not a compression algorithm). Another important distinction is that base 64 does not encrypt any information — it uses a “standard” table of characters to encode and decode information. In other words, any base-64 string can be decoded, as long as the string was encoded using a standard set of characters (which the decoder can also understand). (What Is Base64 Encoding & Decoding?, n.d.)
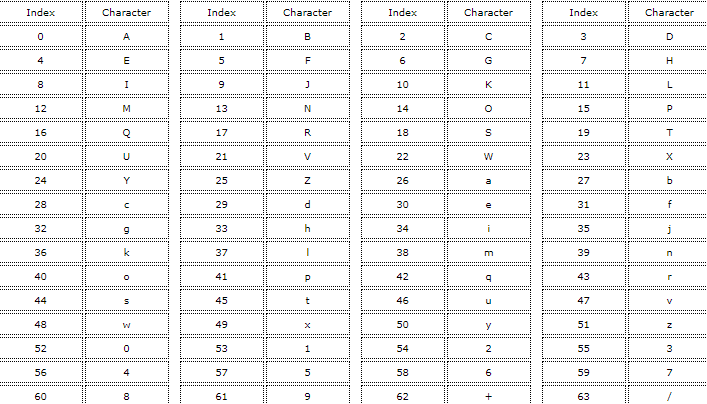
Base64 Index Mapping Table
Base64 Encoding
The encoding algorithm is simple:
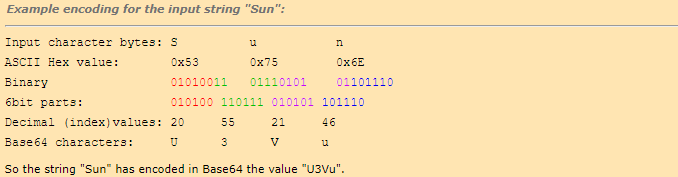
Take three character bytes from the input stream (24bits), divide them into four 6 bit parts and convert each 6 bit value according to the table above. Repeat this until no more input character bytes are left.
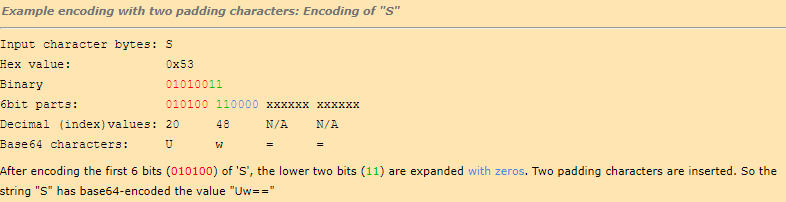
What to do if the number of input character bytes is not divisible by three?
In this case, the input buffer is filled up with zeros until it is divisable by three. Then each 6 bit part which was filled up with zero is encoded with the special padding character ’=‘.
Decoding Base64
Length of a Base64 string
Due to the padding during encoding, the number of characters of a Base64 string is always divisable by four.
Decoding a Base64 string
The decoding process is the reverse of that of the encoding.
References
- What is Base64 Encoding & Decoding? (n.d.). bunny.net. https://bunny.net/academy/http/what-is-base64-encoding-and-decoding/
- Sunshine2k. (n.d.). Sunshine2k’s homepage - Understanding and implementing Base64. http://www.sunshine2k.de/articles/coding/base64/understanding_base64.html