Challenge Description
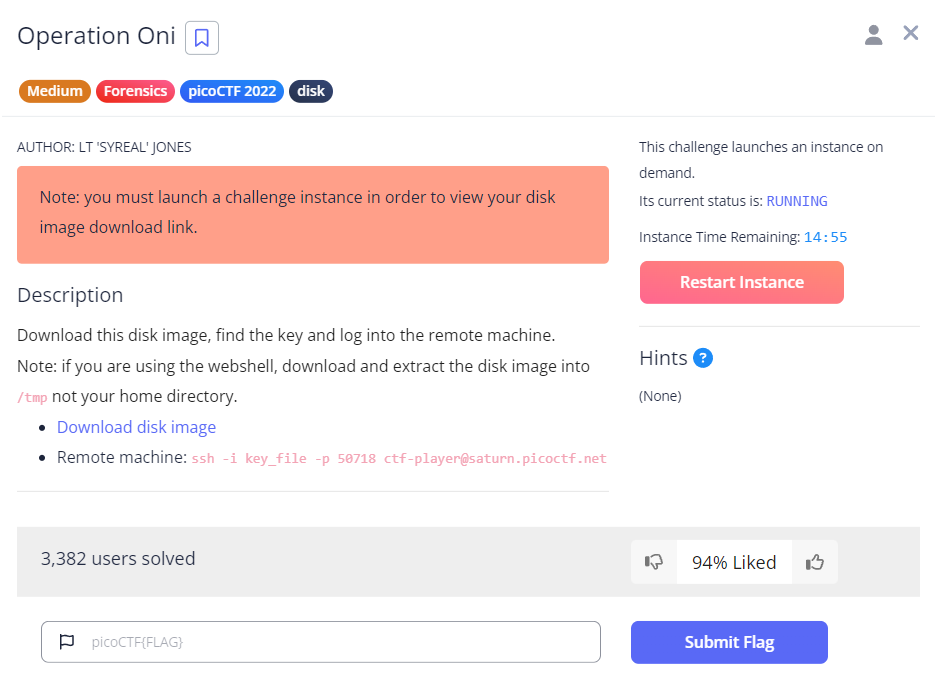
From the description, it looks like we will have to download the disk image and retrieve an ssh key to connect to an ssh server afterwards, in order to obtain our flag.
Download, extract and check the contents
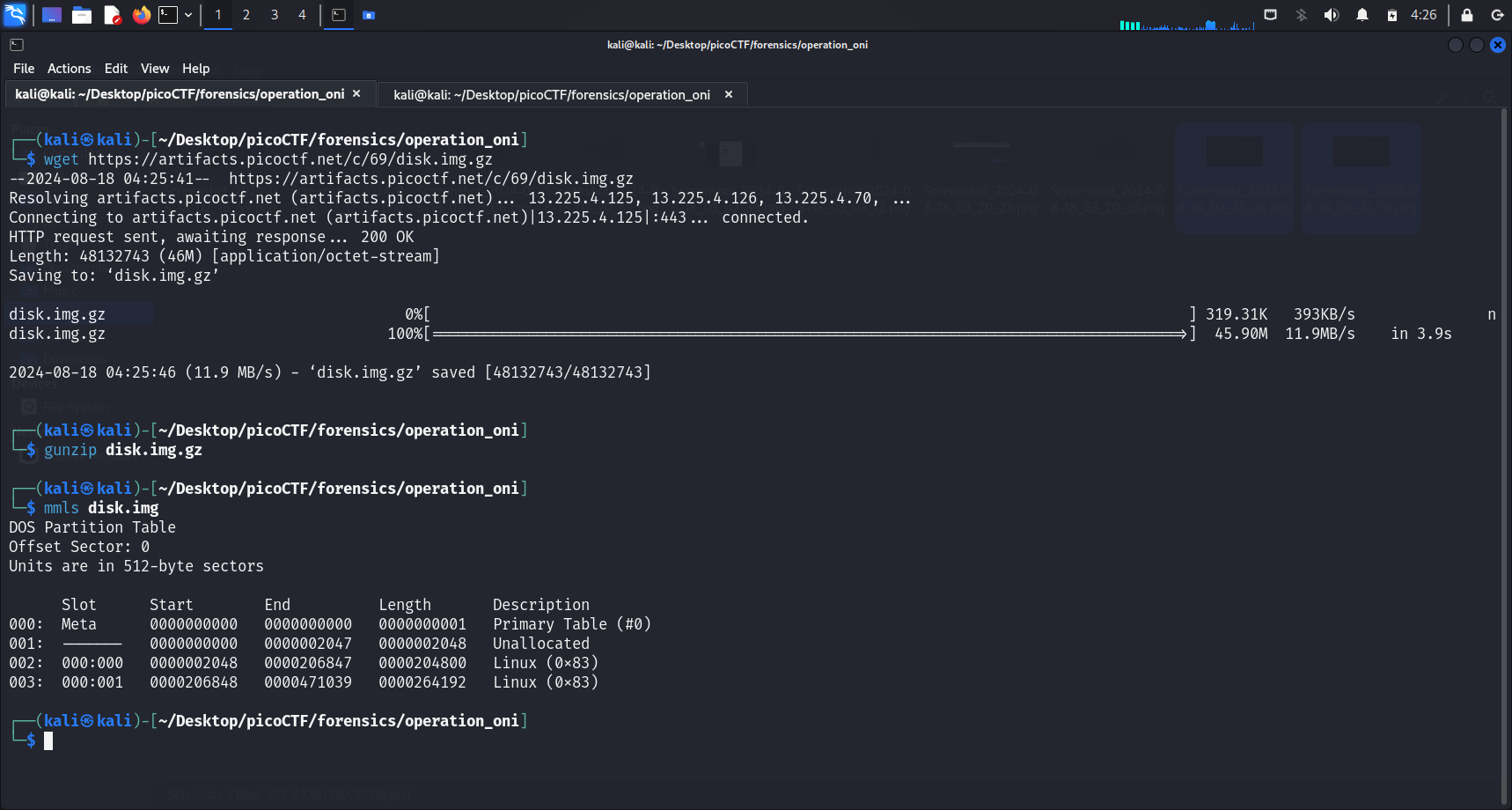 We first download and extract the disk image using
We first download and extract the disk image using wget <link> and gunzip <image-name>. We then run mmls <file-name> to display the partition layout of this volume system. We have to take note of the starting offsets of the different partitions.
Disk Analysis Tool
This challenge will require the usage of disk analysis tools likeThe Sleuth Kit (TSK).
fls command
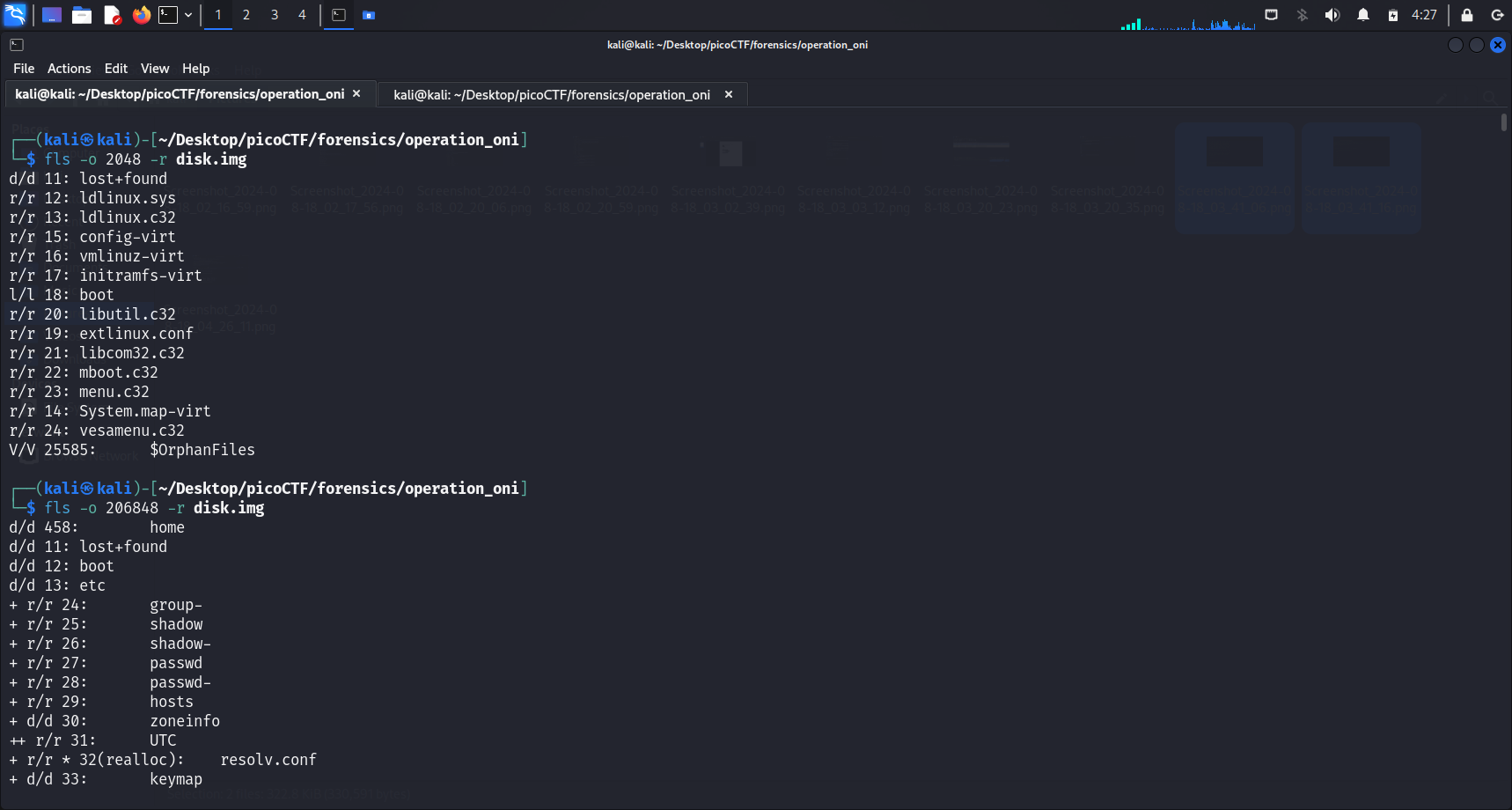 We proceed by running
We proceed by running fls -o <image-offset> -r <image-name> to display the files and directories of the available partitions. It appears that we will have to zoom into the second partition instead of the first, as the first partition does not look like it has the ssh keys.
Location of the SSH keys
According to this source, the ssh keys are normally stored in
~/.sshdirectory. So let’s attemptgrep sshafter we dofls
grep ssh
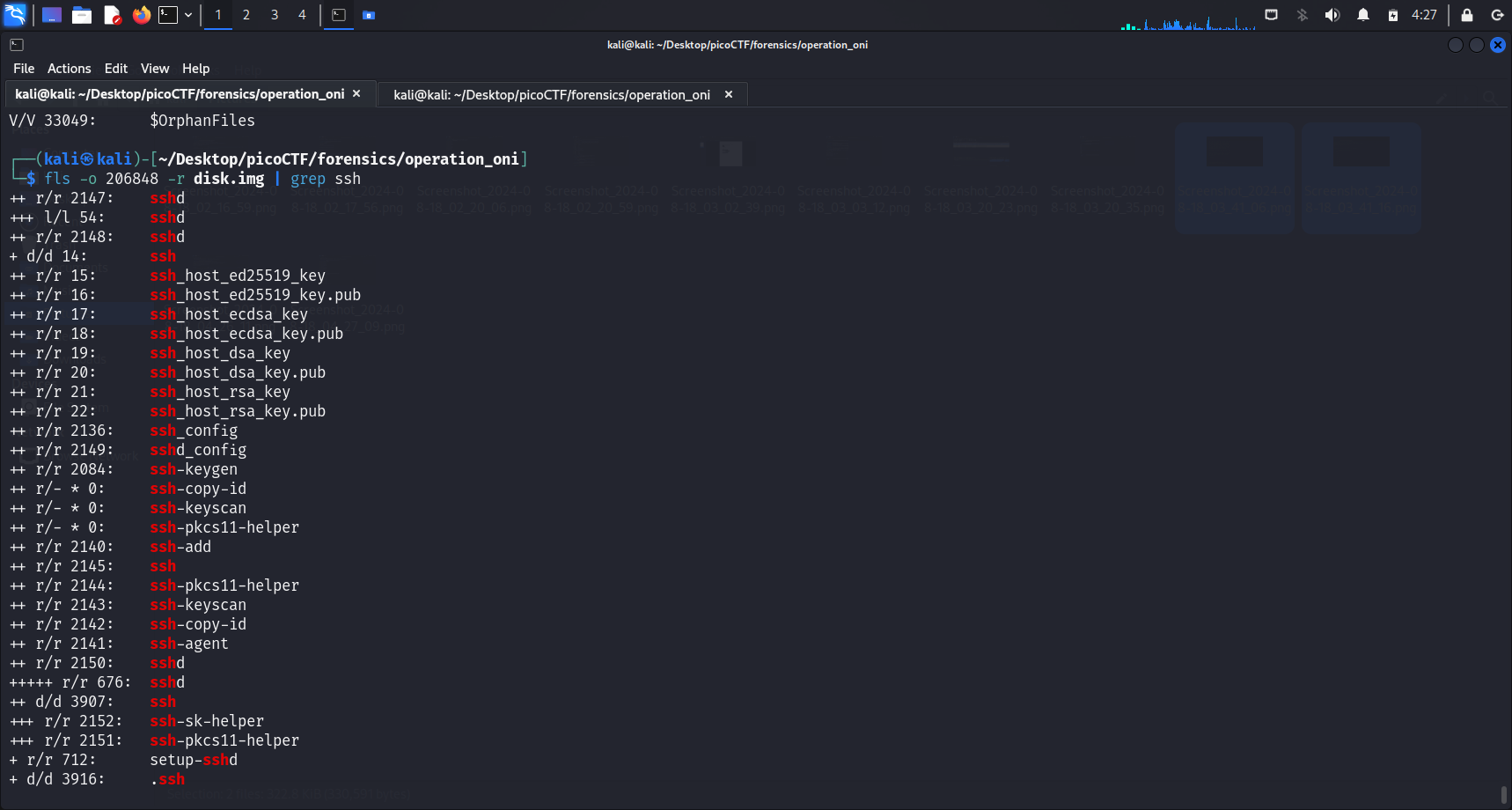
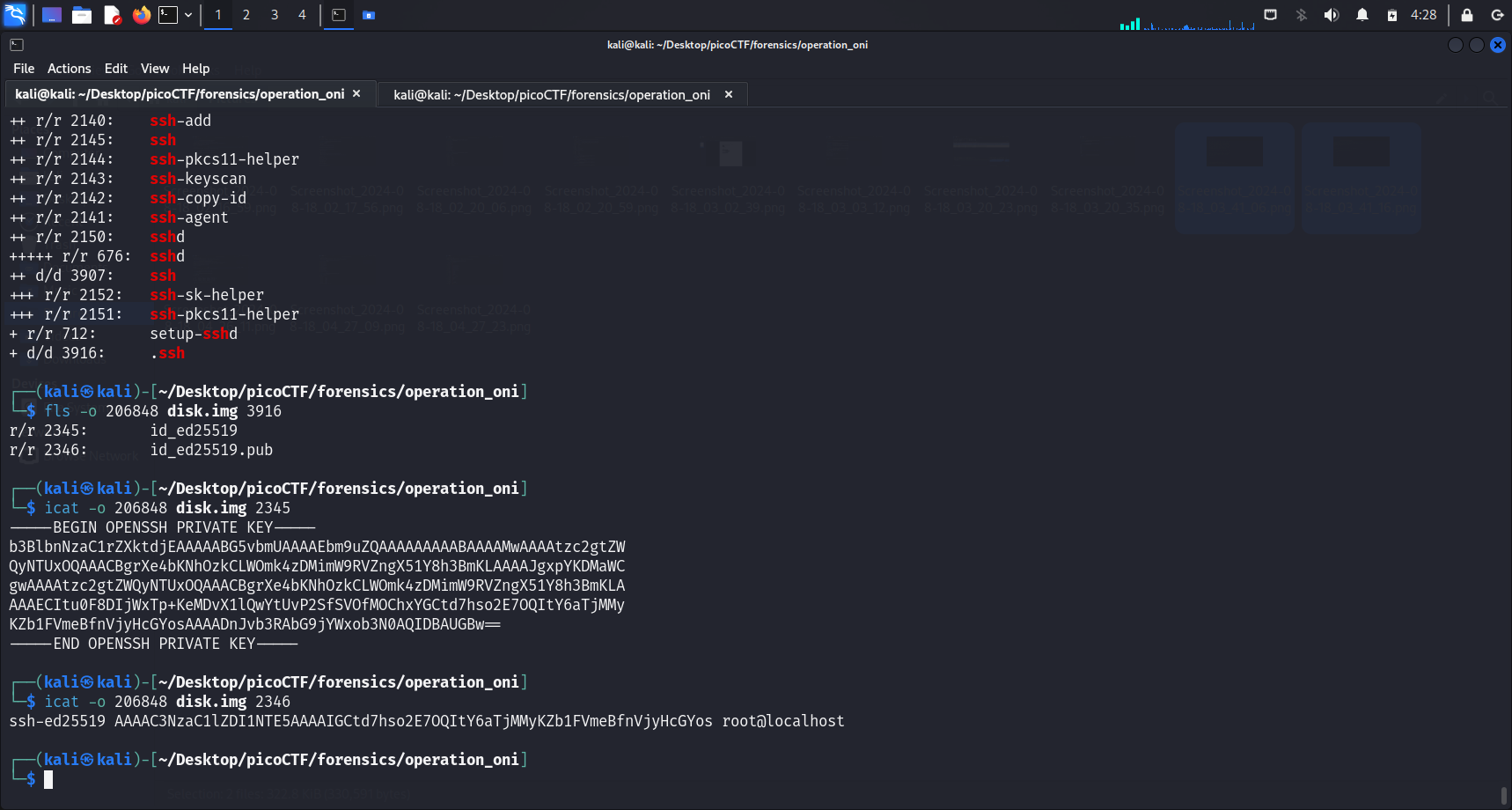
It seems like there are 2 files in the .ssh directory, just as we expected. One should be the public key and the other should be the private one.
Making the output file
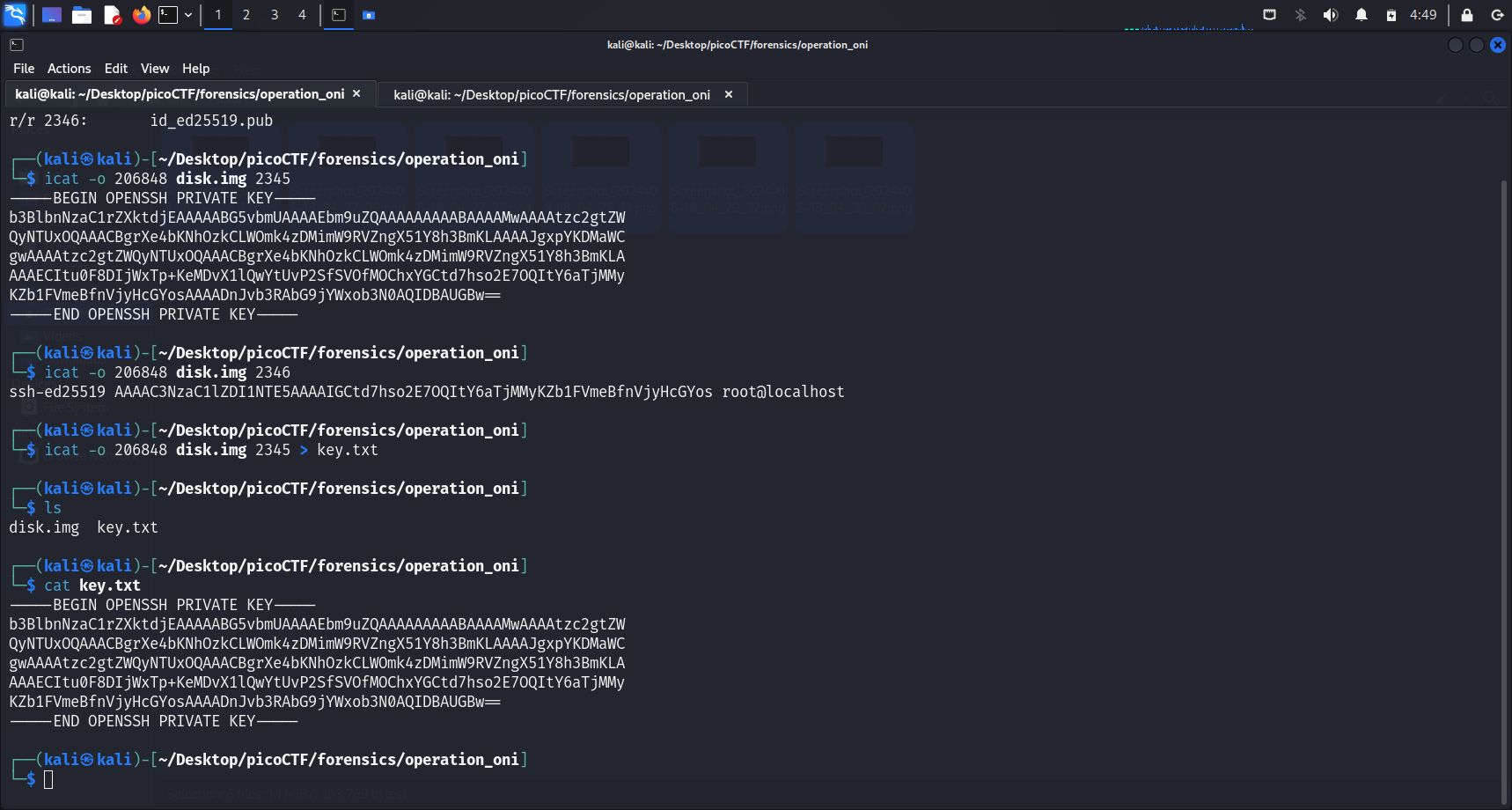
After we ran icat -o 206848 disk.img 2345, it seemed like it contained the full ssh private key, so we shall write the output of this into a key.txt file to connect to the SSH server later on.
Unprotected Private Key File Error
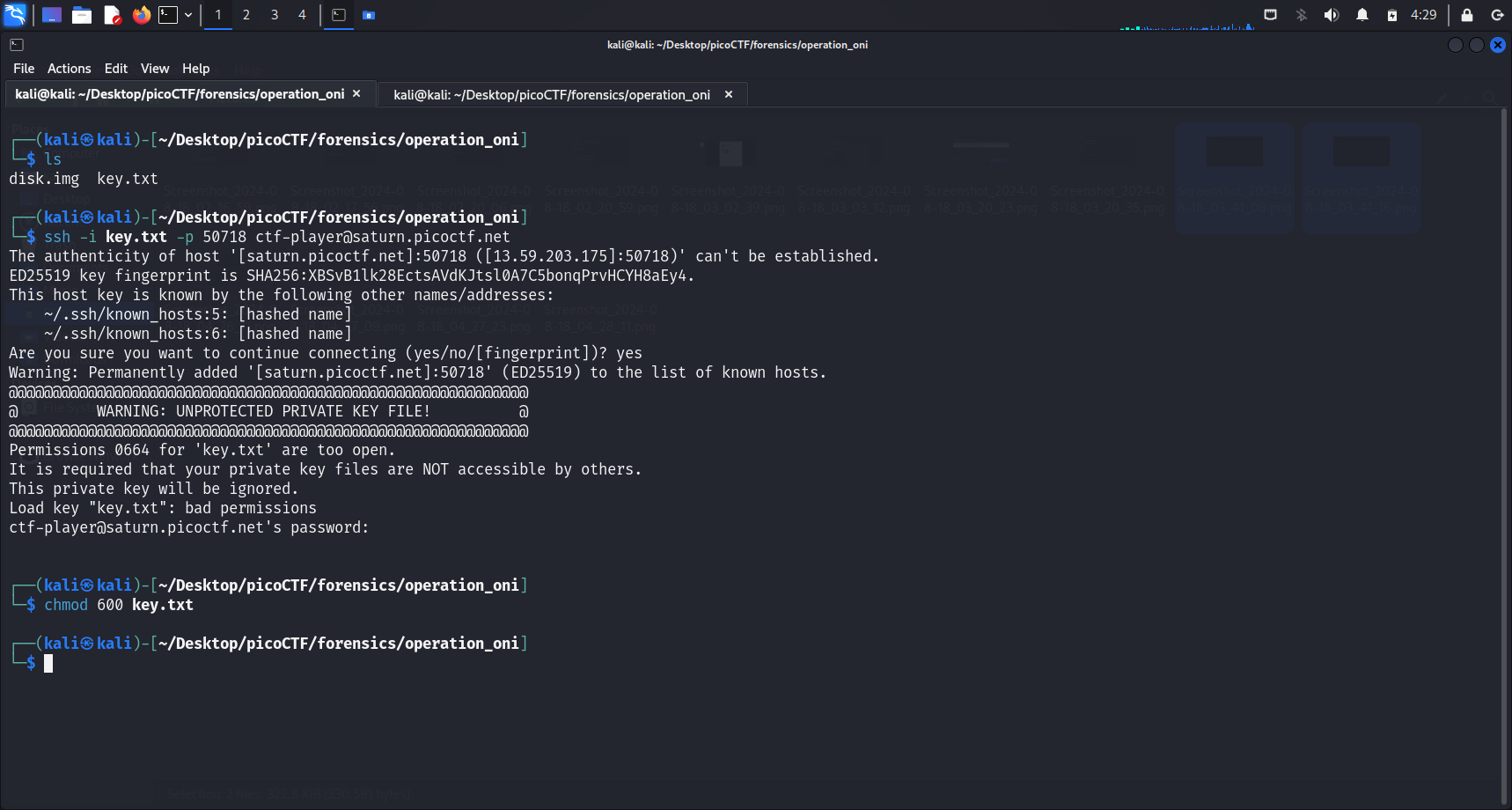
File permissions
Unprotected Private Key File
It is recommended that private key files are NOT accessible by others. To fix this problem, we can run
chmod 600 <file-name>.Understanding
600Permissions
- The permission settings consist of three digits:
- First digit (6): Owner’s permissions.
- Second digit (0): Group’s permissions.
- Third digit (0): Other users’ permissions
- Each digit can be calculated by adding:
- 4: Read permission (
r)- 2: Write permission (
w)- 1: Execute permission (
x)- So,
600translates to:
- 6 (Owner):
rw-(read and write permissions)- 0 (Group):
---(no permissions)- 0 (Others):
---(no permissions)
Connect to SSH server
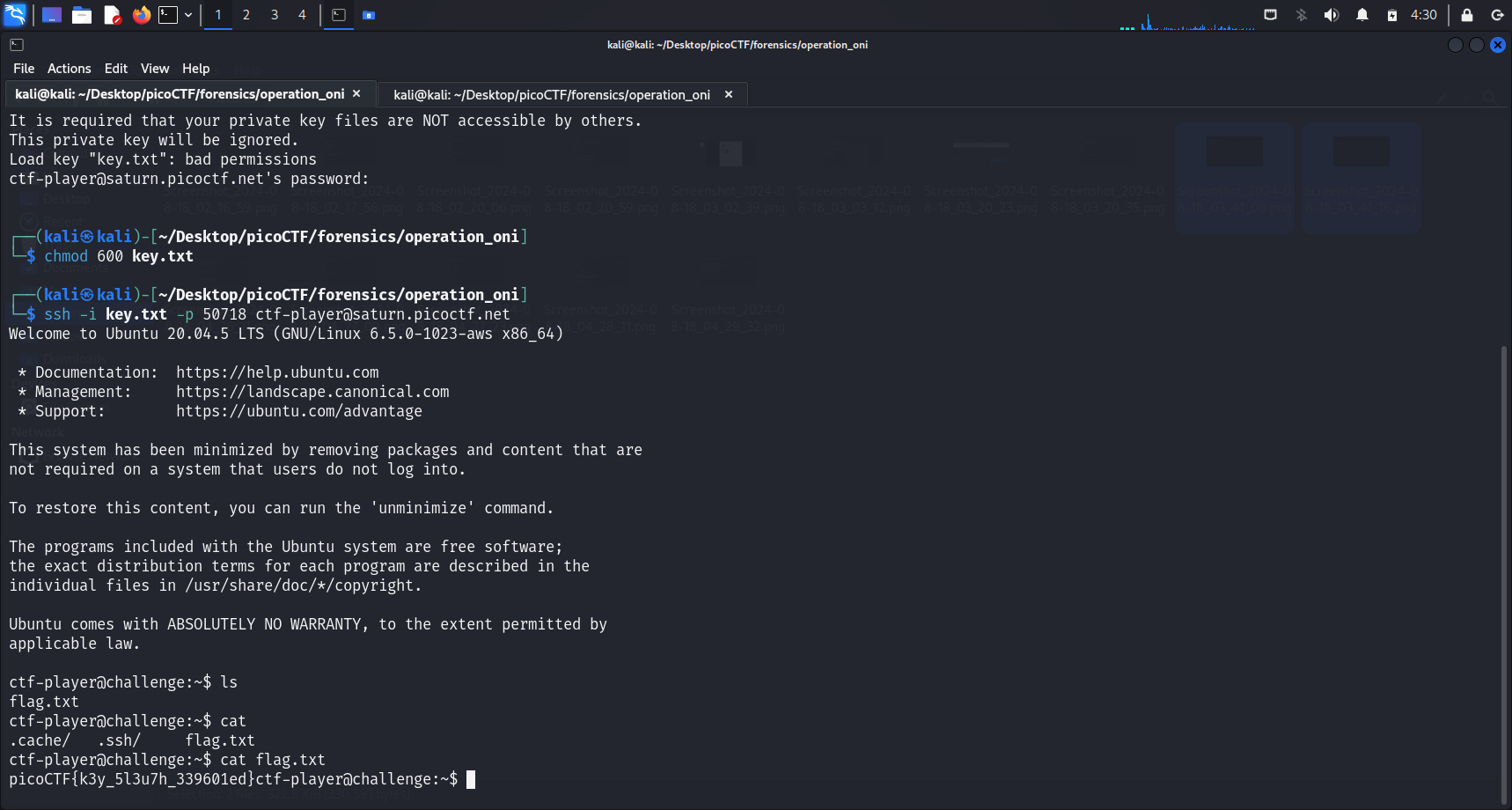 After changing the file permissions, we can successfully connect to the SSH server. We can run
After changing the file permissions, we can successfully connect to the SSH server. We can run ls and cat flag.txt to get our flag.
Flag
picoCTF{k3y_5l3u7h_339601ed}