Challenge Description
Based on the description, we will be dealing with certificate requests in this challenge. Before starting this challenge, I actually had little knowledge about certificate requests. However, I knew about the SSL/TLS handshake for HTTPS and the role that certificate authorities (CAs) play in this handshake.
Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
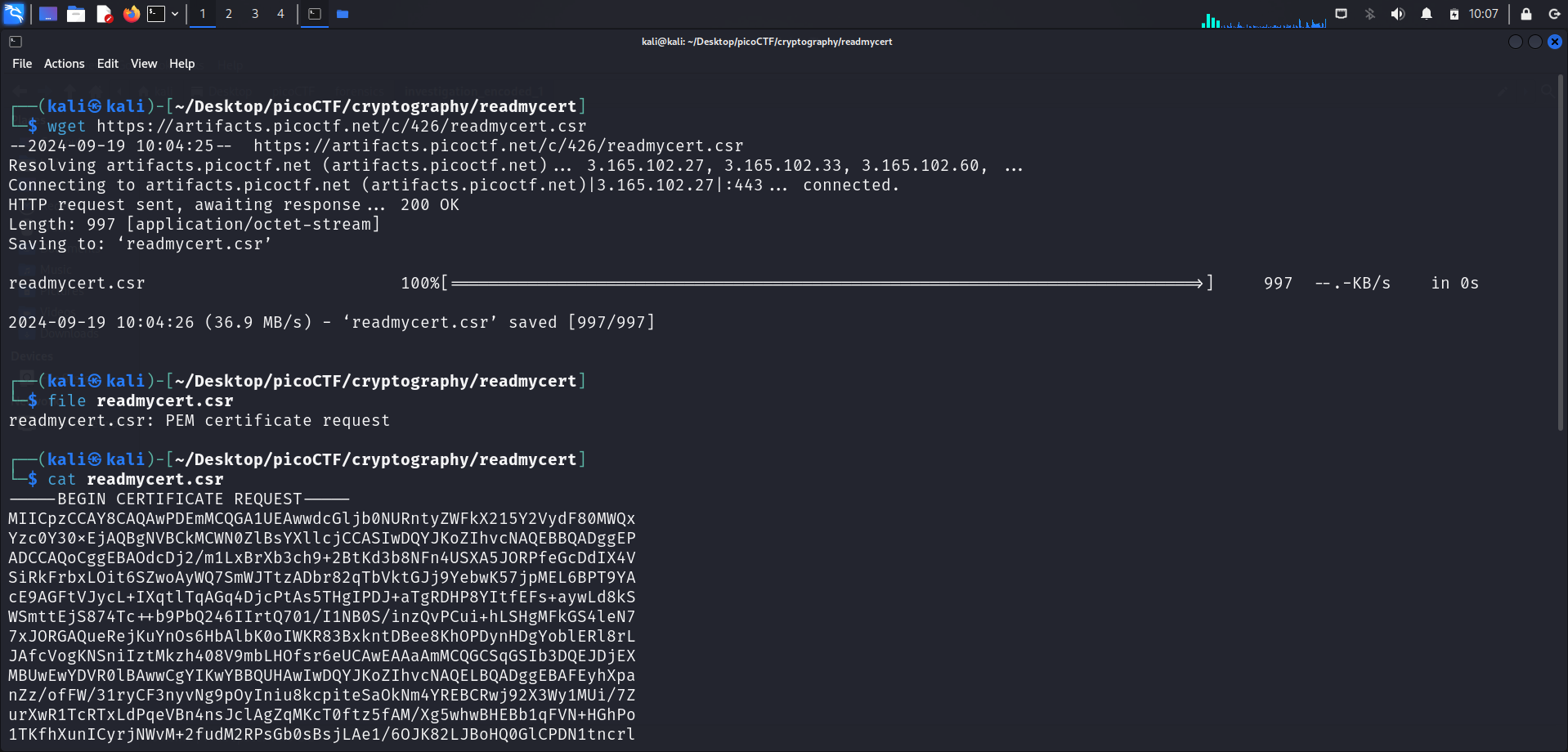
We download the CSR file using wget <link>, as usual. The CSR file is named readmycert.csr.
What is a CSR file?
According to TechTarget, a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) is a specially formatted encrypted message sent from a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) digital certificate applicant to a certificate authority (CA). The CSR validates the information the CA requires to issue a certificate (Shea, 2023).
PicoCTF Hint: Download the certificate signing request and try to read it.
I proceeded by running
cat readmycert.csrto display its contents.
The displayed certificate request is shown below:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
MIICpzCCAY8CAQAwPDEmMCQGA1UEAwwdcGljb0NURntyZWFkX215Y2VydF80MWQx
Yzc0Y30xEjAQBgNVBCkMCWN0ZlBsYXllcjCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEP
ADCCAQoCggEBAOdcDj2/m1LxBrXb3ch9+2BtKd3b8NFn4USXA5JORPfeGcDdIX4V
SiRkFrbxLOit6SZwoAyWQ7SmWJTtzADbr82qTbVktGJj9YebwK57jpMEL6BPT9YA
cE9AGFtVJycL+IXqtlTqAGq4DjcPtAs5THgIPDJ+aTgRDHP8YItfEFs+aywLd8kS
WSmttEjS874Tc++b9PbQ246IIrtQ701/I1NB0S/inzQvPCui+hLSHgMFkGS4leN7
7xJORGAQueRejKuYnOs6HbAlbK0oIWKR83BxkntDBee8KhOPDynHDgYoblERl8rL
JAfcVogKNSniIztMkzh408V9mbLHOfsr6eUCAwEAAaAmMCQGCSqGSIb3DQEJDjEX
MBUwEwYDVR0lBAwwCgYIKwYBBQUHAwIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQADggEBAFEyhXpa
nZz/ofFW/31ryCF3nyvNg9pOyIniu8kcpiteSaOkNm4YREBCRwj92X3Wy1MUi/7Z
urXwR1TcRTxLdPqeVBn4nsJclAgZqMKcT0ftz5fAM/Xg5whwBHEBb1qFVN+HGhPo
1TKfhXunICyrjNWvM+2fudM2RPsGb0sBsjLAe1/6OJK82LJBoHQ0GlCPDN1tncrl
lpzHACCFPv7LMVF9BSkZDCQNglU1NYDDelXZezfXLbio/a1RC2k4rs+jorVmFese
elZFzORDsCzlgD87NvBUMZWI8J5+9fZeaWAQQfhwEiZOVn8IcjLUxUraxt4rbI/h
0EUJJuCjGyTjRpQ=
-----END CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
Base64?
I found the output above very interesting, although it looked like gibberish. There was a familiar “=” at the end of the certificate request portion, and I instinctively thought of Base64. This is because the special character “=” is used for padding in Base64 encoding.
Hence, I made another file named request.txt, which only contained the certificate request portion (without the begin and end). I also combined the lines to form a single line as such:
MIICpzCCAY8CAQAwPDEmMCQGA1UEAwwdcGljb0NURntyZWFkX215Y2VydF80MWQxYzc0Y30xEjAQBgNVBCkMCWN0ZlBsYXllcjCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAOdcDj2/m1LxBrXb3ch9+2BtKd3b8NFn4USXA5JORPfeGcDdIX4VSiRkFrbxLOit6SZwoAyWQ7SmWJTtzADbr82qTbVktGJj9YebwK57jpMEL6BPT9YAcE9AGFtVJycL+IXqtlTqAGq4DjcPtAs5THgIPDJ+aTgRDHP8YItfEFs+aywLd8kSWSmttEjS874Tc++b9PbQ246IIrtQ701/I1NB0S/inzQvPCui+hLSHgMFkGS4leN77xJORGAQueRejKuYnOs6HbAlbK0oIWKR83BxkntDBee8KhOPDynHDgYoblERl8rLJAfcVogKNSniIztMkzh408V9mbLHOfsr6eUCAwEAAaAmMCQGCSqGSIb3DQEJDjEXMBUwEwYDVR0lBAwwCgYIKwYBBQUHAwIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQADggEBAFEyhXpanZz/ofFW/31ryCF3nyvNg9pOyIniu8kcpiteSaOkNm4YREBCRwj92X3Wy1MUi/7ZurXwR1TcRTxLdPqeVBn4nsJclAgZqMKcT0ftz5fAM/Xg5whwBHEBb1qFVN+HGhPo1TKfhXunICyrjNWvM+2fudM2RPsGb0sBsjLAe1/6OJK82LJBoHQ0GlCPDN1tncrllpzHACCFPv7LMVF9BSkZDCQNglU1NYDDelXZezfXLbio/a1RC2k4rs+jorVmFeseelZFzORDsCzlgD87NvBUMZWI8J5+9fZeaWAQQfhwEiZOVn8IcjLUxUraxt4rbI/h0EUJJuCjGyTjRpQ=
Decoding
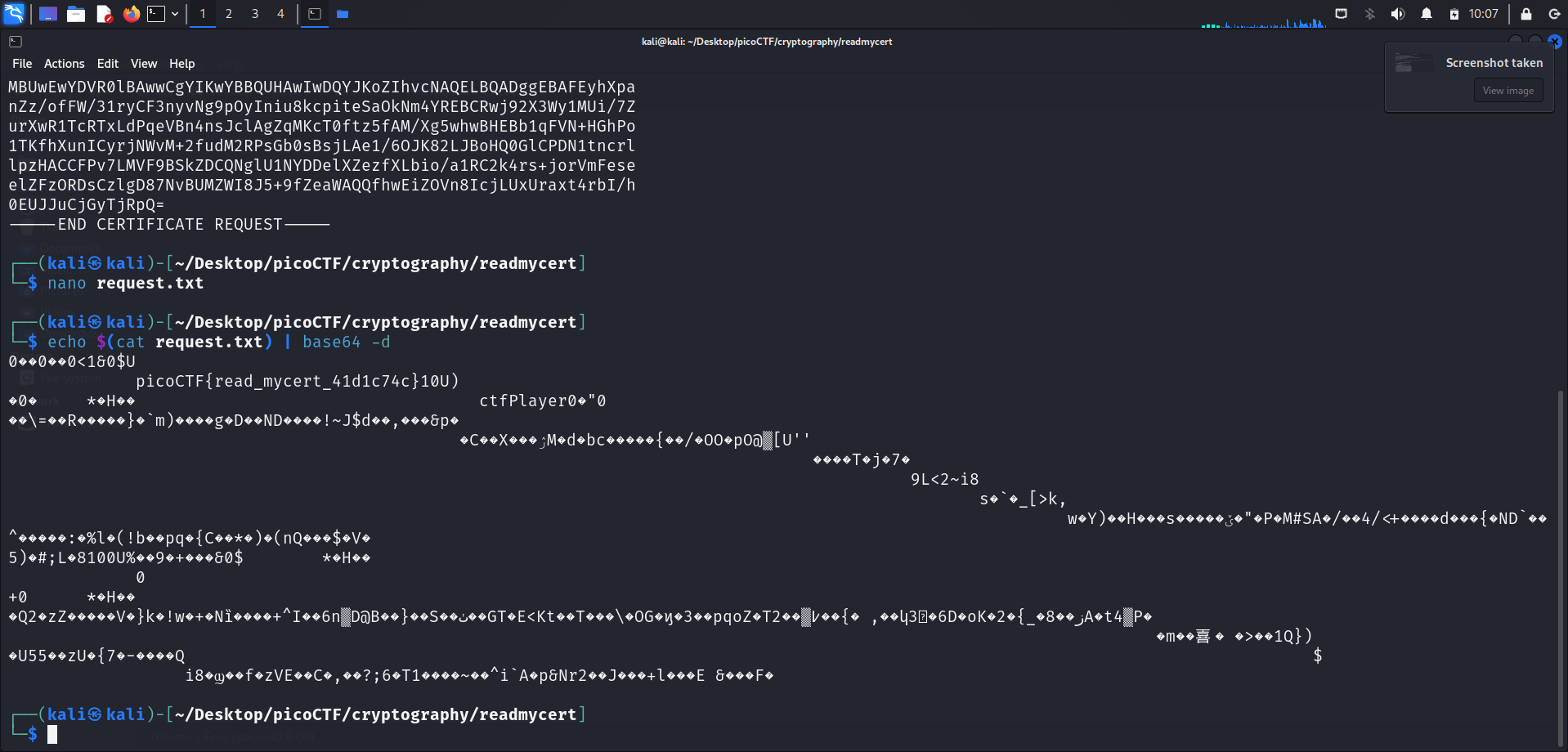
To decode the contents of request.txt, I ran this command:
echo $(cat request.txt) | base64 -dThis command decodes a base64-encoded string found in request.txt and outputs the decoded content. -d is used here to decode the contents of request.txt.
Running this command displays this:
0��0��0<1&0$U
picoCTF{read_mycert_41d1c74c}10U)
�0� *�H�� ctfPlayer0�"0
��\=��R�����}�`m)����g�D��ND����!~J$d��,���&p�
�C��X���ۯM�d�bc�����{��/�OO�pO@▒[U''
����T�j�7�
9L<2~i8
s�`�_[>k,
w�Y)��H���s�����ێ�"�P�M#SA�/��4/<+����d���{�ND`��^�����:�%l�(!b��pq�{C��*�)�(nQ���$�V�
5)�#;L�8100U%��9�+���&0$ *�H��
0
+0 *�H��
�Q2�zZ�����V�}k�!w�+�Nȉ����+^I��6n▒D@B��}��S��ٺ��GT�E<Kt��T���\�OG�ϗ�3��pqoZ�T߇▒��2��{� ,��կ3ퟹ�6D�oK�2�{_�8��زA�t4▒P�
�m��喜� �>��1Q})
�U55��zU�{7�-����Q $
i8�ϣ��f�zVE��C�,��?;6�T1����~��^i`A�p&Nr2��J���+l���E &���F� At first glance, it seems like the output is just plain gibberish. However, upon closer inspection, we can see the flag being hidden in the output.
Flag
picoCTF{read_mycert_41d1c74c}
References
- Shea, S. (2023, March 30). CSR (Certificate Signing Request). Security. https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/CSR-Certificate-Signing-Request#:~:text=A%20CSR%20(Certificate%20Signing%20Request)%20is%20a%20specially%20formatted%20encrypted,a%20certificate%20authority%20(CA).