Challenge Description
Honestly, I did not have much knowledge about endianness and what exactly is Big-Endian and Little-Endian before this challenge. This challenge was a good introduction to the concept for me.
What is endianness?
I was able to get a basic understanding of endianness from these 2 sources:
Basically, endianness refers to the order in which bytes are arranged in computer memory. In a Big-Endian system, the most significant byte (MSB) is stored at the smallest memory address, and the least significant byte (LSB) at the largest. A Little-Endian system is of course the opposite, with the LSB at the smallest memory address and the MSB at the largest.
MSB
The above image from the GeeksforGeeks source mentioned earlier clarifies the difference between LSB and MSB.
Basically, of the 2 endian systems, big-endian is closer to the way we read words in English, from left to right.
Little endian and big endian representations of a word
I first downloaded the provided file, which was a program written in C programming language. I ran cat to examine the code.
After reading the code, I realised that a user will be given a string of random characters ( which they call a “word”), and our task is to return the little-endian and big-endian representations of the “word”. We will be given the flag only if both representations are correct.
PicoCTF Hint: You might want to check the ASCII table to first find the hexadecimal representation of characters before finding the endianness.
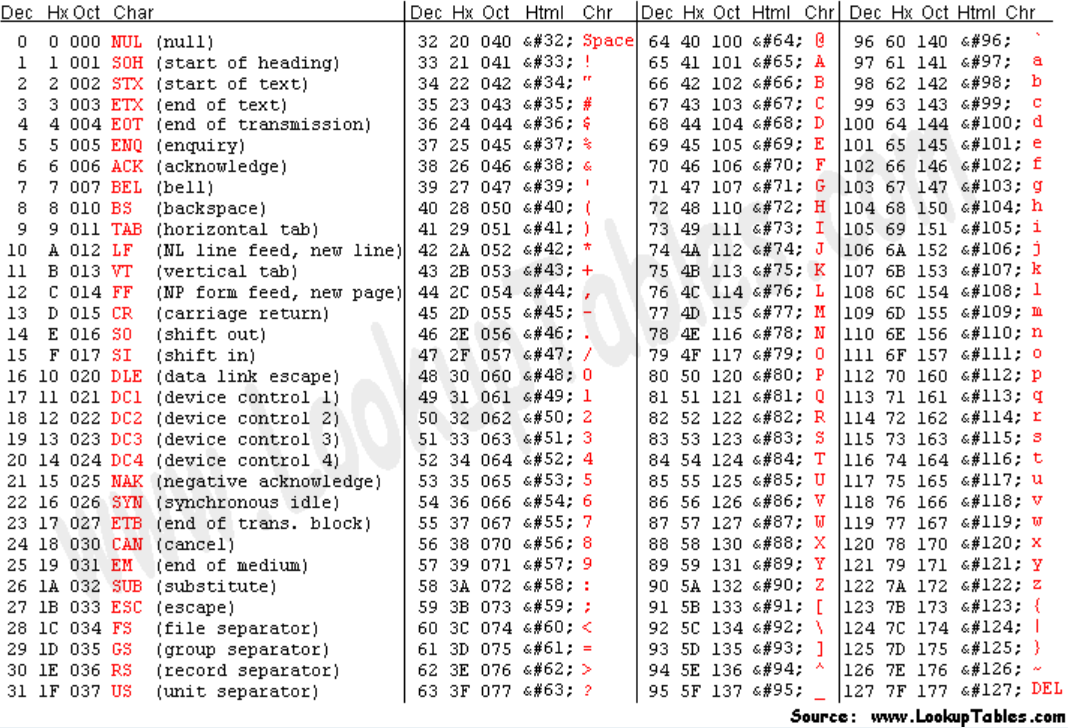
We know that in ASCII encoding, 1 character corresponds to a single byte (8 bits). In the hexadecimal or base-16 system, 2 characters represent 1 byte. In the ASCII table, we can easily convert a character into its hexadecimal value. From there. we can easily derive the little endian and big endian representations of the “word” given. I’ll provide a brief walkthrough below.
Suppose that we have a string “
abc”. Using the ASCII table shown below, the hexadecimal values ofa,bandcare 61, 62 and 63 respectively.In the little-endian system, the LSB is at the smallest memory address, and the MSB is at the largest. So, the little-endian representation of the string will be
636261. You can think of it as reading in reverse, starting at the back.The big-endian representation is the opposite of the one in the little-endian system. In this case, the big-endian representation if
616263, just like how we are used to reading from left to right in English.
Putting concepts into practice
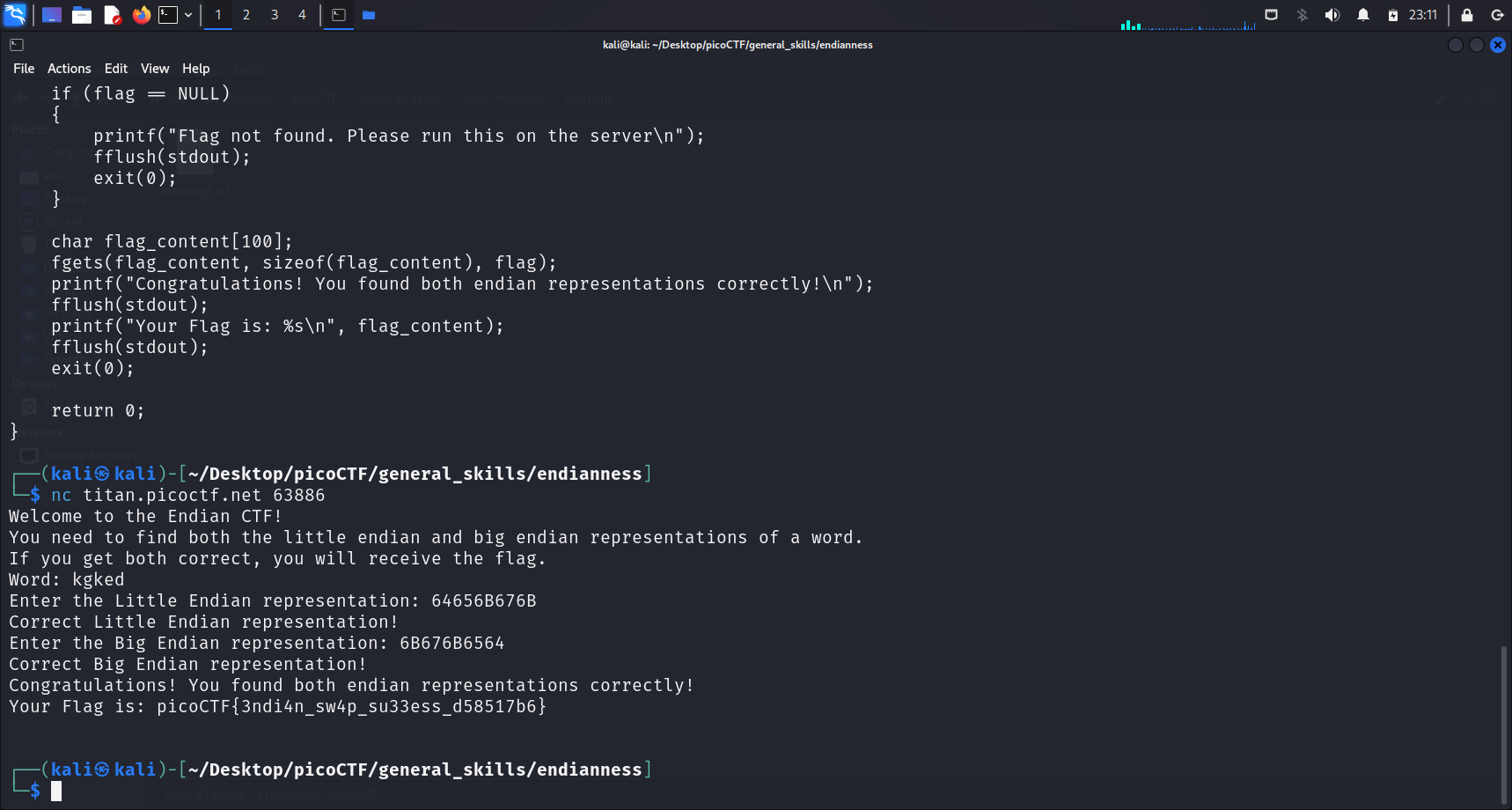
Using the same concept, I ran the command given when I launched an instance to connect to their server.
Once connected, I was given this “word”, kgked. I used the ASCII table shown above to convert each character into its hexadecimal representation
k: 6Bg: 67k: 6Be: 65d: 64
The little-endian representation is 64656B676B and the big-endian representation is 6B676B6564. Submitting these as input allowed me to get the flag.
Flag
picoCTF{3ndi4n_sw4p_su33ess_d58517b6}
References
- Endianness. (2024, July 7). Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endianness
- GeeksforGeeks. (2024c, May 23). What is Endianness? BigEndian & LittleEndian. GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/little-and-big-endian-mystery/
- Tutorial: Character Encoding. (n.d.). https://dsc.gmu.edu/tutorials-data/tutorial-character-encoding/#:~:text=Just%202%20hex%20characters%20can,prefixed%20with%200x%20%2C%20like%200xC8%20.
