Challenge Description
Description
An IT staff on the internal network (10.0.0.0/24) reported unauthorised data transfers! We managed to capture some network traffic from the affected segment, and initial analysis suggests that a host was compromised via a payload download and is now maintaining a persistent Command-and-Control (C2) connection…
Your task is to perform further investigation. You should identify 2 crucial indicators, which are the C2 IP address and the beacon interval. Do note that the beacon interval should be a whole number i.e. no decimal places.
The flag should be submitted in the following format: HNF25{IP_Interval} e.g. HNF25{1.2.3.4_20}
- Author: Jun Wei
- Category: forensics
- Difficulty: medium
Files
Beaconing - Solution
For this challenge, participants are given a file called capture.pcap. There are 2 values they need to include in the flag:
- C2 IP address
- Beacon interval (how frequent does the malware communicates and sends “check in” requests to the C2 server)
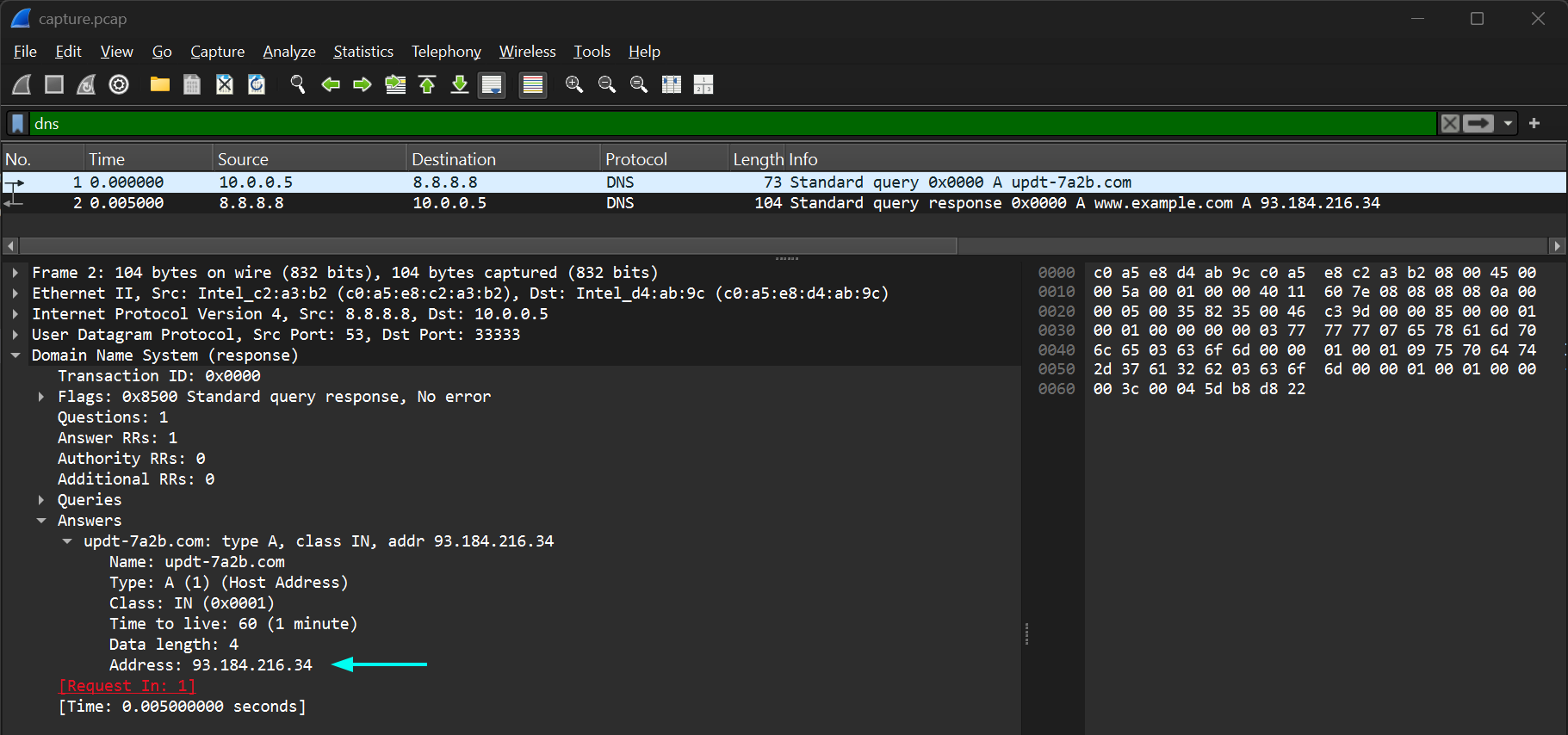
- To find the suspicious C2 IP address, look for queries resolving non-standard domains. This should direct us to the query for updt-7a2b.com, which is the C2 domain.
-
We can extract the C2 IP address from the DNS query returned. The C2 IP address is identified as 93.184.216.34.
-
The malware (called
payload.exe) is downloaded on the victim computer, and seems to communicate via HTTP to an external C2 server. We can use a filter likeip.addr == 93.184.216.34to filter for network traffic with the C2 server.
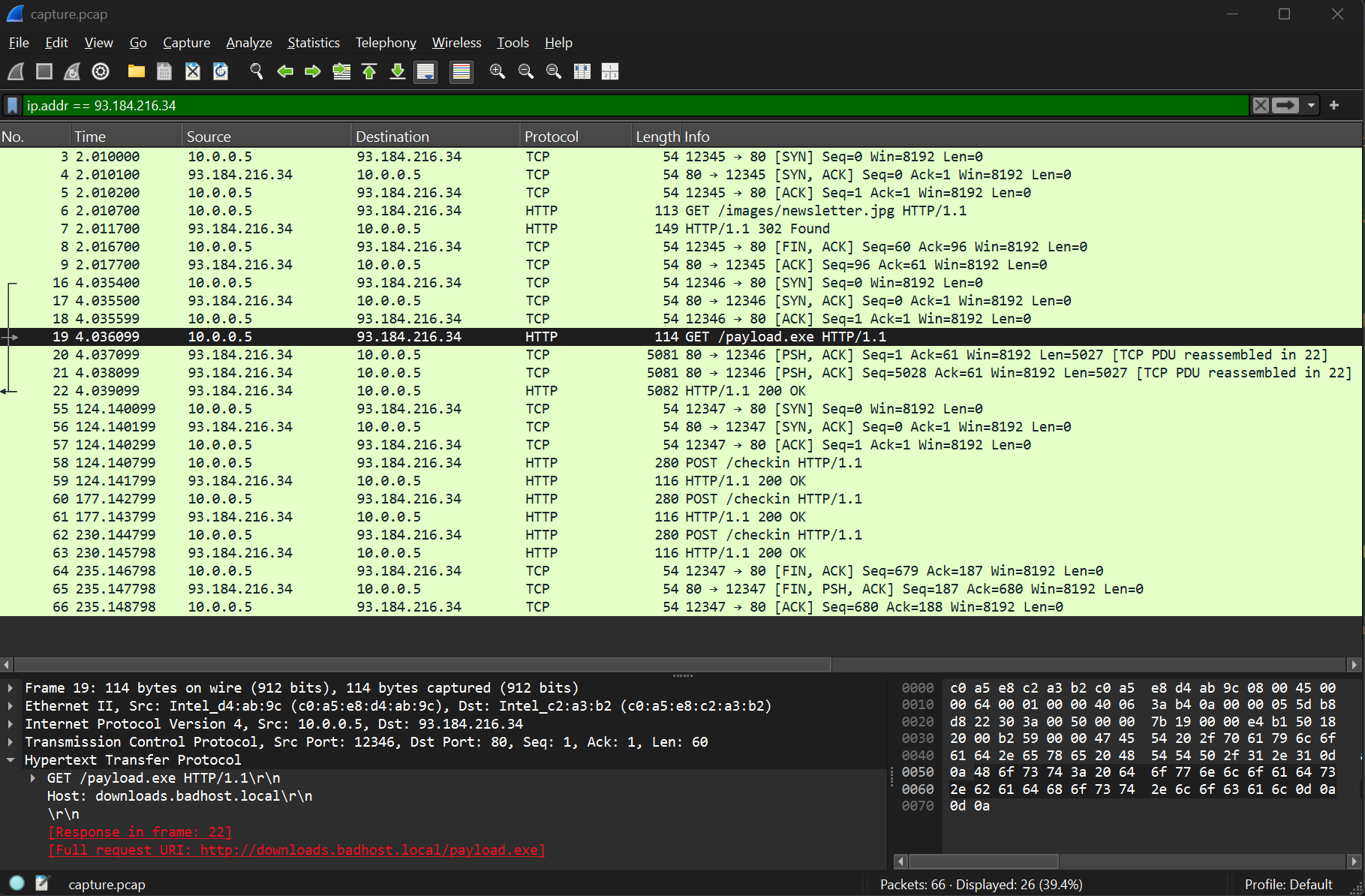
- The HTTP POST requests are the C2 beacons. We can analyze the headers and content to confirm this is malicious persistence activity.
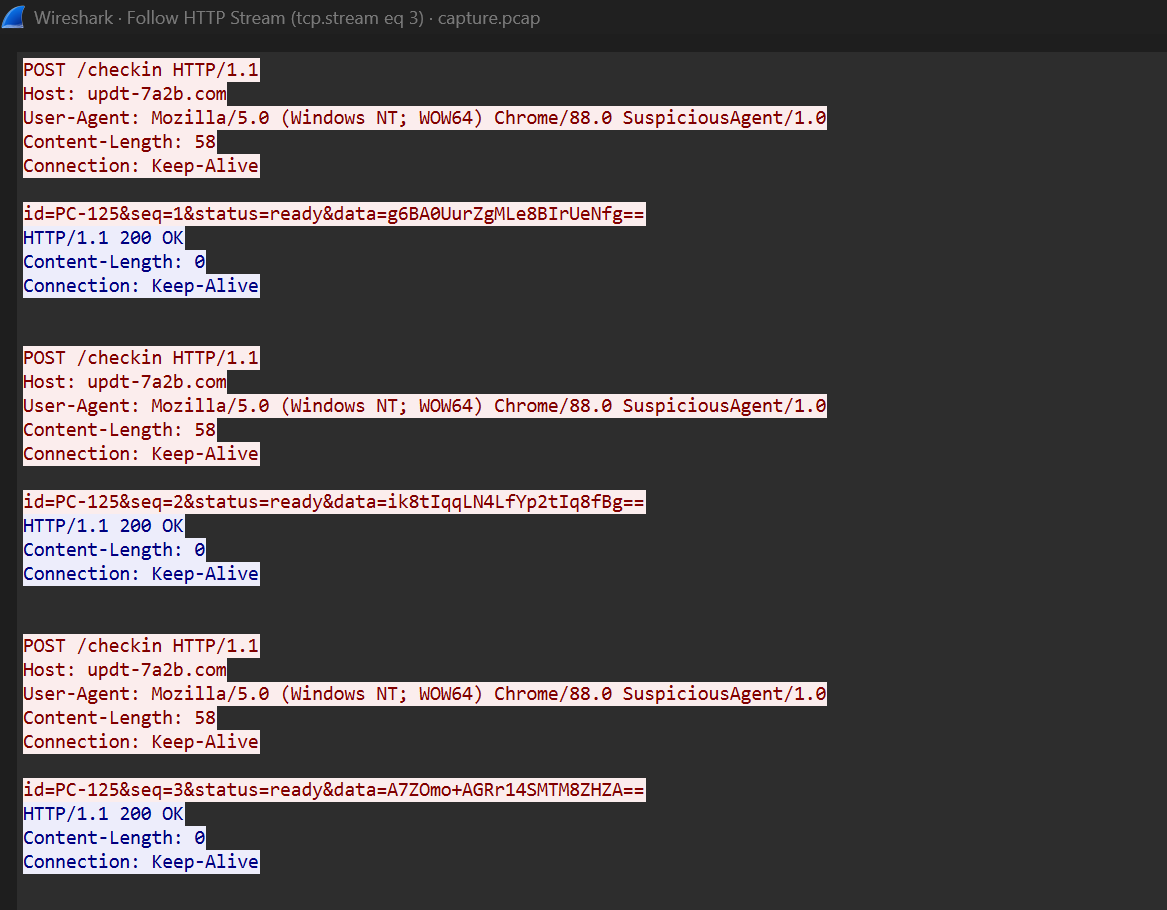
- The requests hit the URI /checkin, which seems unusual for legitimate web traffic.
- The User-Agent string is modified for malware fingerprinting:
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT; WOW64) Chrome/88.0 SuspiciousAgent/1.0.- The appended SuspiciousAgent/1.0 is a strong indicator of compromise.
- The POST body contains a structured, encoded payload, confirming it’s a scheduled status report from the malware.
- To find the beacon interval, we can inspect the timestamps for the 3 identified C2 POST requests. We will need to find the difference in time between the requests to calculate the interval. This can be done by subtracting the timestamp of the first beacon from the second, or the second from the third.
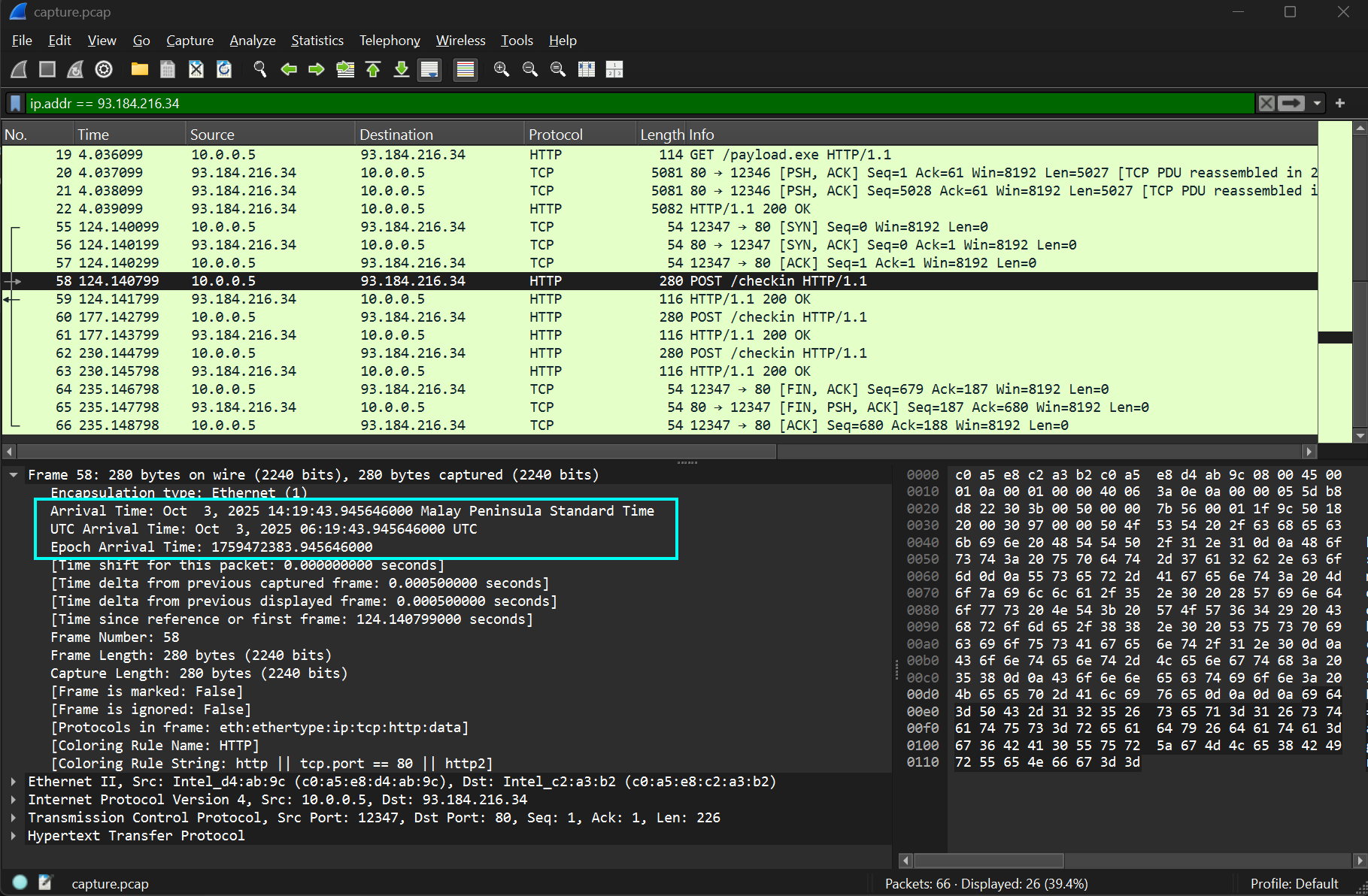
The beacon interval should be 53 seconds.
Flag: HNF25{93.184.216.34_53}